4th Feb every year is observed as World Cancer Day. Every year a theme is decided for this day. The 2024 World Cancer Day theme is: ‘Close the Care Gap’.
Promoting awareness about cancer and encouraging early detection are crucial steps in improving outcomes and reducing the burden of the disease. The theme highlights the significance of ensuring that individuals, regardless of their geographic location, economic status, or other factors, have access to timely and appropriate cancer prevention, screening, diagnosis, and treatment services.
As a urologist & robotic cancer surgeon, I treat cancers of prostate, urinary bladder, kidneys, testes and penis. Today, I will discuss about the prostate cancer. If Are you looking for the Best Urology Hospital in Delhi NCR at You can visit the Madhuban Kidney Care.
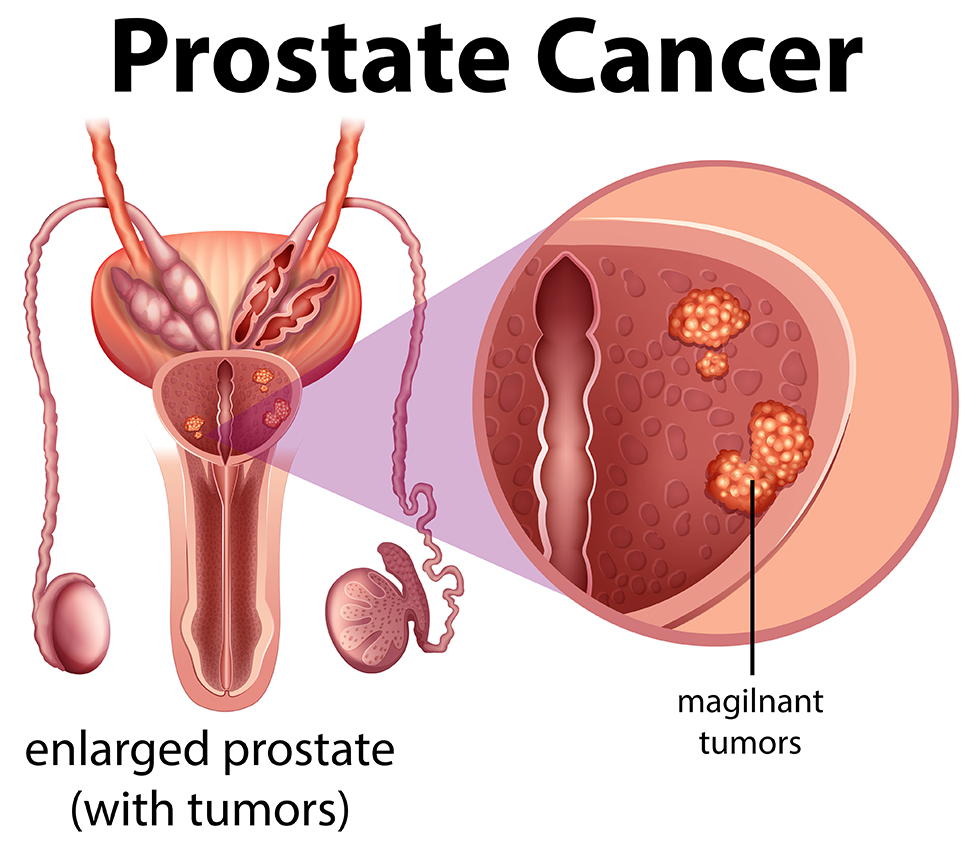
Prostate cancer is a type of cancer that develops in the prostate, a small walnut-shaped gland in men that produces seminal fluid. The stages, diagnosis, and treatment of prostate cancer can vary based on the extent of the disease. It’s important to note that only a healthcare professional can provide specific advice tailored to an individual’s case. Here’s a general overview:
Stages of Prostate Cancer:
- Stage I: Cancer is confined to the prostate and is not palpable during a digital rectal exam (DRE). It is usually detected incidentally during surgery for another prostate condition.
- Stage II: Cancer is still confined to the prostate but can be felt during a DRE.
- Stage III: Cancer has spread beyond the prostate capsule but has not reached distant organs.
- Stage IV: Cancer has spread to nearby tissues, lymph nodes, or other organs such as bones.
Diagnosis:
- Digital Rectal Exam (DRE): A physical examination where a healthcare provider checks for any abnormalities or lumps in the prostate through the rectum.
- Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Test: Measures the level of PSA in the blood. Elevated PSA levels can be a sign of prostate issues, but not all elevated PSA levels indicate cancer.
- Biopsy: If other tests suggest prostate cancer, a biopsy is often performed. A small tissue sample is taken from the prostate and examined under a microscope to confirm the presence of cancer.
- Imaging Studies: Imaging tests such as MRI, PET-CT scans, or bone scans may be done to determine the extent of cancer spread.
Treatment:
- Active Surveillance: For low-risk cancers, especially in older individuals, monitoring may be recommended without immediate treatment.
- Surgery (Prostatectomy): Removal of the prostate gland may be recommended, especially for early-stage cancers. Presently it is done using Robotic technology; as a result the recovery is very fast and minimal after effects.
- Radiation Therapy: High-energy rays are used to target and kill cancer cells. This can be delivered externally or through implanted radioactive seeds.
- Hormone Therapy: Reducing the levels of male hormones (androgens) can slow the growth of prostate cancer.
- Chemotherapy: Medications are used to kill cancer cells, often reserved for advanced cases.
- Immunotherapy: Boosts the body’s immune system to fight cancer.
- Targeted Therapy: Targets specific molecules involved in cancer growth.
The choice of treatment depends on factors such as the stage of cancer, overall health, and patient preferences. It’s important for individuals diagnosed with prostate cancer to discuss options thoroughly with their healthcare team to make informed decisions about their care. Regular follow-ups are essential to monitor the response to treatment and address any potential side effects or complications.
Image Sourses : Click Here